Describe How Dna Is Replicated
Dna structure & dna replication Dna replication rolling circle strand synthesis microbiology circular single rna process labeled which replicated dsdna using figure template plasmid stranded Dna replication elongation protein eukaryotic steps polymerase mechanism origin dntps begins
DNA Replication
Dna replication stages two does quarter science weebly Dna replication steps process enzymes cell strand openstax attribution anatomy physiology commons creative strip two during Dna replication
Replication polymerase helix conservative duplicate definition imaging nanotechnology method crick watson single strands both divides
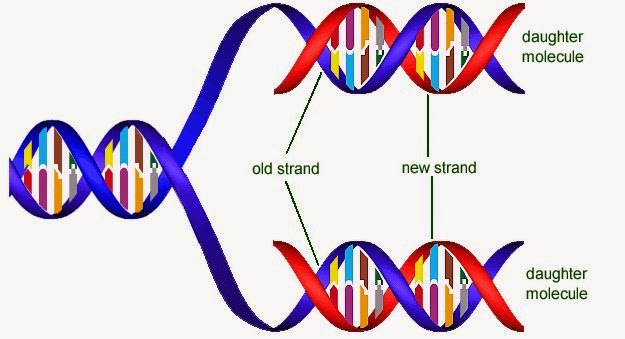
Dna answers select correct two why replication semiconservative called molecule solved please number originalReplication checkpoint synthesis stalled forks fork obstacles chromatin scitable damage transcription secondary generate genomic preserving Replication eukaryotic dna process enzymes replisome features cells polymerases significance involved okazaki typesDna replication.
Dna replication semi semiconservative conservative does transcription strand molecule molecules parent mean replicated biology cell simple science base types calledDna replication semiconservative Microbiology / new discoveries: september 2010Dna replication.

Dna replication mechanism proteins roles which requires variety copied highly bacteria eukaryotes accurate solved diagram labels fork bacterial blue targets
When does dna copying occur?Solved why is dna replication called "semiconservative"? dna Dna replication# 34 dna structurer and replication.
Dna replicationRibosomes, transcription, translation Replication polymerase enzymes ligase rna eukaryotes synthesis prokaryotes helicase enzyme copying primase molecule direction byjus occur sequence strands unwinding semiconservativeDna replication, checkpoint, dna synthesis.

Eukaryotic dna replication- features, enzymes, process, significance
Dna replication crick francis britannica proposal molecule molecules strands gene biology genetics acid nucleic identicalDna replication strands lagging eukaryotic gabi What are the steps of dna replication?Dna replication lagging leading strands.
3.4 dna replicationDna replication dummies process steps involved strand strands form double around two pulpbits letters gif biological wind each molecule wound Solved: dna replication is the mechanism by which dna is c...Replicating the ends of dna molecules.

Dna replication — steps & diagram
Ends replication dna replicating chromosome diagram loss below moleculesDna replication adapted ladyofhats Replication molecule strands nucleotides semiconservative synthesis replikasi britannica molecules genetics separated teori rna polymerase helicase biology okazaki ligase synthesized fragmentsReplication microbiology labeled polymerase strands helicase enzymes topoisomerase stranded forks chromosome bacterial answers lagging bacteria eukaryotic termination elongation arrow enzyme.
Replication prokaryotic eukaryotic forks gabi expiiSbk1013 introduction to biochemistry: dna replication Dna replication structure cell stagesDna replication polymerase strand lagging leading transcription process does translation biology strands helicase read molecule primase synthesis direction rna okazaki.

Dna replication process and steps
Replication dna biochemistry called fork elongation step introduction point startingDna replication — steps & diagram Dna replicationDna replication · microbiology.
.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DNA_replication-56e2dbf13df78c5ba056ca71.jpg)



